Grid computing - distributed computing
Grid computing - distributed computing
Grid computing can be defined as a type of parallel and distributed system that enables sharing, selection, and aggregation of geographically distributed autonomous resources. Grid resources are assigned dynamically at runtime depending on their availability and capability.
Many people confuse between grid computing, distributed computing, and computational clusters. You have 10 computers somewhere that can be used for distributed calculations of your model, and people already call it a grid, most likely because the word grid is easy to work with and sounds good too. It does not really matter much, but for the sake of clarity, IT perfectionalists like to distinguish between a grid and the others.
What is Grid Computing?
Grid Computing, or the use of a computational grid (workstations, blade servers, etc.) is defined as the application of resources of multiple computers in a network to a single problem at the same time, while crossing political and theoretical boundaries. A true grid comprises multiple distinct distributed processing environments.
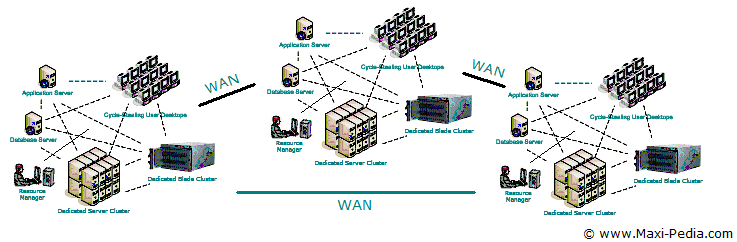
Picture: Grid computing employs not only single resources but whole systems from various locations while crossing geographic and political boundaries.
Grid computing virtualizes the processing resources of multiple computers for use towards a single problem, either through dedicated or shared hardware. What this means is that your grid-enabled application is not tied to the computer on your desk, it can seamlessly use more than one computer and other resources even beyond the walls of your building to boost its performance.
What is Distributed Computing?
Distributed Computing, or the use of a computational cluster, is defined as the application of resources from multiple computers, networked in a single environment, to a single problem at the same time - usually to a scientific or technical problem that requires a great number of computer processing cycles or access to large amounts of data.
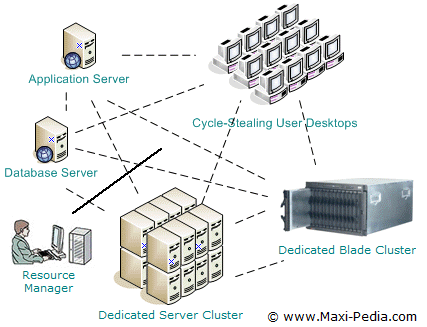
Picture: The concept of distributed computing is simple -- pull together and employ all available resources to speed up computing.
The key distinction between distributed computing and grid computing is mainly the way resources are managed. Distributed computing uses a centralized resource manager and all nodes cooperatively work together as a single unified resource or a system. Grid computing utilizes a structure where each node has its own resource manager and the system does not act as a single unit.Is it a grid or distributed?
The terms distributed computing and grid computing are being used interchangeably. When people talk about "grid", they usually talk about a solution that looks more like what we picture above for the distributed computing. It is probably for the simplicity of expression. It is easier to say "grid" than to say "distributed computing environment" when talking about the application. It is not a big deal, and if all the business people call the network in their company a grid, then let it be a grid. So, let's take a look at how people set up their "grids". This can be found on the next page: Cycle stealing (grid/distributed computing).
It is easy, just include the code provided below into your HTML code.
 Delicious
Delicious Digg
Digg StumbleUpon
StumbleUpon Furl
Furl Facebook
Facebook Google
Google Yahoo
Yahoo